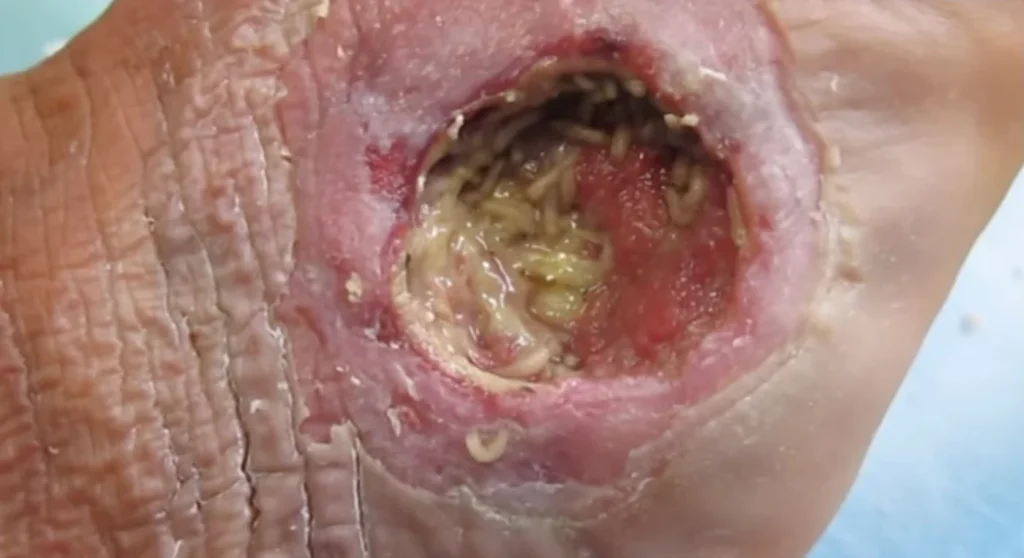
Maggot removal from a wound, also known as myiasis, involves several steps and can be managed using various methods.
It’s crucial to remove maggots promptly to prevent infection and further tissue damage.
Here’s a general overview of how to manage maggot infestations:
- 1. Initial Assessment and Preparation:
- Identify the wound: Determine the location and extent of the infestation.
- Gather supplies: You’ll need sterile gloves, gauze pads, saline solution, forceps, a collection bag, and potentially hydrogen peroxide or other cleaning agents.
- 2. Wound Irrigation and Maggot Removal:
- Irrigate the wound: Gently flush the wound with saline to dislodge maggots.
- Remove maggots: Use forceps to extract any visible maggots. Collect them in a bag for proper disposal.
- Consider using a temporary dressing: A film dressing can help suffocate any remaining maggots, allowing for easier removal later.
- 3. Wound Cleaning and Debridement:
- Clean the wound: After removing maggots, clean the wound thoroughly with saline or other recommended solutions.
- Consider hydrogen peroxide: In some cases, hydrogen peroxide can be used to stun or weaken maggots, making them easier to remove.
- Surgical debridement: If necessary, a surgeon may remove the maggots or surrounding tissue surgically, especially if the infection is severe or the maggots are deeply embedded.
- 4. Monitoring and Treatment:
- Observe for signs of infection: Keep a close watch for any signs of infection, such as increased pain, redness, swelling, or pus.
- Treat infection: If infection develops, seek medical attention for appropriate antibiotic treatment.
- Maggot debridement therapy: In certain cases, sterile maggots (from a medical source) may be used for debridement, helping to remove dead tissue and promote healing.
Important Considerations:
- Avoid leaving wild maggots in the wound:Wild maggots can carry bacteria and other microbes, increasing the risk of infection.
- Proper disposal:Always dispose of maggots in a sealed bag or container to prevent further infestation.
- Seek professional help:If you’re unsure about how to manage a maggot infestation, seek medical attention.
Additional Tips:
- Use sterile equipment: Always use sterile gloves and tools to minimize the risk of infection.
- Follow instructions carefully: If you’re using hydrogen peroxide or other cleaning agents, follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully.
- Keep the wound clean and dry: This helps to prevent further infestation and promote healing.
Disclaimer: This information is for general knowledge and should not be taken as medical advice.
Consult with a healthcare professional for any health concerns or before making any decisions related to your health or treatment.






