Life StyleStoryTrending
Trending
Acne is a common skin condition characterized by the occurrence of comedones (blackheads and whiteheads),
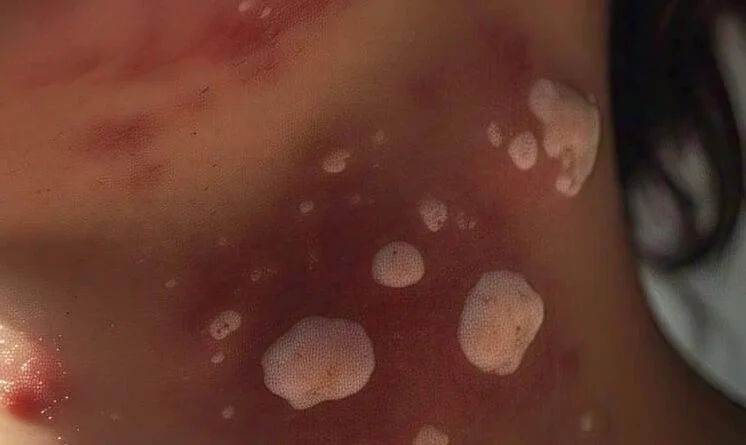
It affects people of all ages, but it’s most prevalent during puberty, adolescence, and young adulthood.

Types of Acne:
- Blackheads: Open comedones with a black appearance due to oxidized melanin.
- Whiteheads: Closed comedones with a white appearance.
- Papules: Pink or red bumps caused by inflammation.
- Pustules: Similar to papules but filled with pus.
- Nodules: Large, painful bumps under the skin.
- Cysts: Large, painful bumps filled with pus.
Causes of Acne
- Hormonal fluctuations: During puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause.
- Genetics: Family history plays a role.
- Stress: Increases cortisol levels, leading to acne.
- Medications: Certain drugs, such as corticosteroids and testosterone.
- Diet: Consuming dairy products, refined carbohydrates, and foods high in sugar.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to pollution, humidity, and certain chemicals.
Symptoms:
- Inflammation: Redness, swelling, and pain.
- Scarring: Permanent marks on the skin.
- Emotional distress: Low self-esteem, anxiety, and depression.
- Topical treatments: Benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, and retinoids.
- Oral antibiotics: For moderate to severe acne.
- Hormonal treatments: Birth control pills or spironolactone.
- Retinoid therapy: Derivatives of vitamin A.
- Blue light therapy: Targets bacteria causing acne.
- Extraction: Removing blackheads and whiteheads.
- Maintain good hygiene: Wash your face twice a day.
- Use non-comedogenic products: Avoid oil-based products.
- Avoid picking or popping pimples: Prevents scarring and infection.
- Keep hands away: Prevents transferring bacteria.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water.
- Acne persists or worsens.
- Scarring occurs.
- You experience emotional distress.
Early treatment can help alleviate symptoms and prevent long-term consequences. Would you like more information on acne or specific treatments?






