
Ear infections are often associated with children, but did you know they can affect adults too? In fact, it’s estimated that 20% of adults experience ear infections at some point in their lives. Whether caused by bacteria, viruses, or other factors, ear infections don’t discriminate based on age, and it’s important for everyone—regardless of age—to recognize the symptoms early to ensure quick treatment and prevent further complications.
In this article, we’ll explore six crucial signs of an ear infection, discuss how to manage it, and provide helpful tips for prevention. By understanding these symptoms and taking proactive steps, you can help protect your hearing and maintain overall ear health.
What is an Ear Infection?
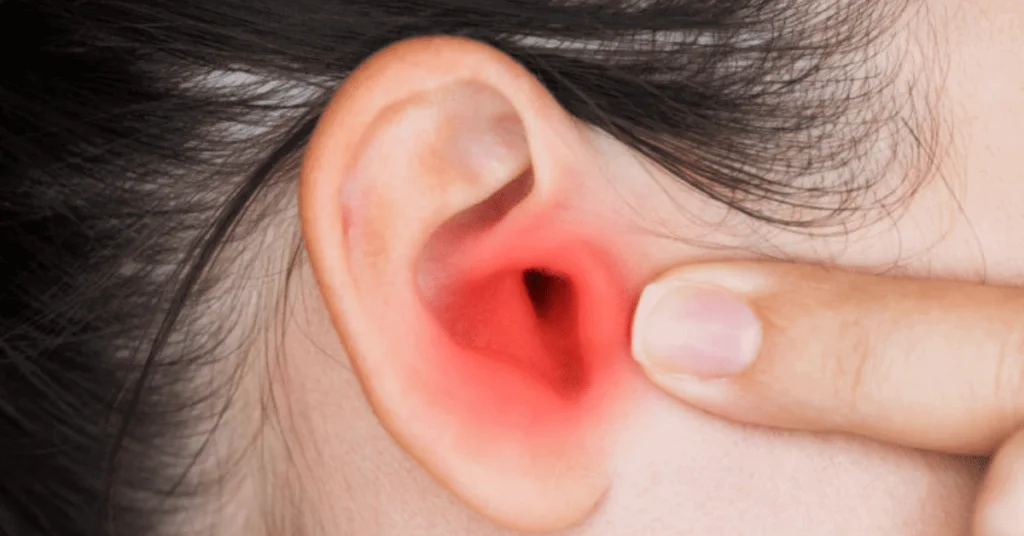
Before diving into the symptoms, it’s helpful to understand what an ear infection is. An ear infection occurs when bacteria or viruses infect the ear canal, middle ear, or the small structures inside the ear. These infections can occur in one or both ears and often lead to inflammation, fluid buildup, and discomfort. Ear infections can result from a variety of causes, including sinus infections, colds, allergies, or even excess moisture from swimming.
Although ear infections are often more common in children, adults can be affected as well. Some people may experience frequent ear infections, while others may develop them only occasionally. If left untreated, ear infections can lead to complications such as hearing loss or chronic infections. That’s why it’s important to be aware of the warning signs and seek timely treatment.
6 Crucial Signs of an Ear Infection
1. Mild Itchiness in the Inner Ear Canal
Itchiness inside the ear canal can often be one of the first signs of an ear infection. This sensation occurs as the infection begins to irritate the sensitive skin of the ear canal. In the early stages, the itchiness may be mild and intermittent. However, if the infection progresses and inflammation sets in, the itching may worsen, making it harder to resist scratching.
If you find yourself frequently itching your ears, or if the itching becomes persistent or bothersome, it’s important to consult your doctor. Early detection can prevent the infection from worsening and reduce the risk of complications.
2. Redness and Swelling
As an ear infection progresses, redness may begin to appear in or around the ear. This is usually a sign of inflammation caused by the infection. You may notice redness on the outer ear or inside the ear canal.
If you spot any unusual redness or swelling, especially if it’s accompanied by pain, it’s time to seek medical attention. Swelling can sometimes cause discomfort or affect your hearing, and leaving it untreated may lead to more severe complications, such as a ruptured eardrum or chronic infections.
3. Discomfort or Pain in the Ear
One of the most common and well-known symptoms of an ear infection is discomfort or pain. This pain may range from mild to severe and can occur suddenly or gradually. In some cases, it may feel like a dull ache, while in other cases, it can be sharp and intense.
If the pain is located in the middle ear (behind the eardrum), it may be due to fluid buildup caused by the infection. This fluid can put pressure on the ear structures, leading to pain and discomfort. The pain might be more noticeable when you touch or tug on the ear, or when you lie down.
Ear pain can often be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers, but if the pain persists for more than a couple of days, or if it worsens over time, it’s essential to get it checked by a healthcare professional to avoid complications.
4. Hearing Loss or Muffled Hearing
Another sign of an ear infection is a temporary loss of hearing or muffled hearing. When the ear becomes inflamed, fluid may accumulate in the middle ear, making it difficult for sound to travel properly. This can result in a feeling of fullness or a “clogged” ear.
In some cases, this muffled hearing may subside once the infection is treated and the fluid drains away. However, prolonged or untreated infections may lead to more severe hearing problems, including long-term hearing loss.
If you notice a decrease in your hearing ability, it’s important to seek medical care. Early treatment can help prevent any lasting damage and restore normal hearing.
5. Fluid Drainage from the Ear
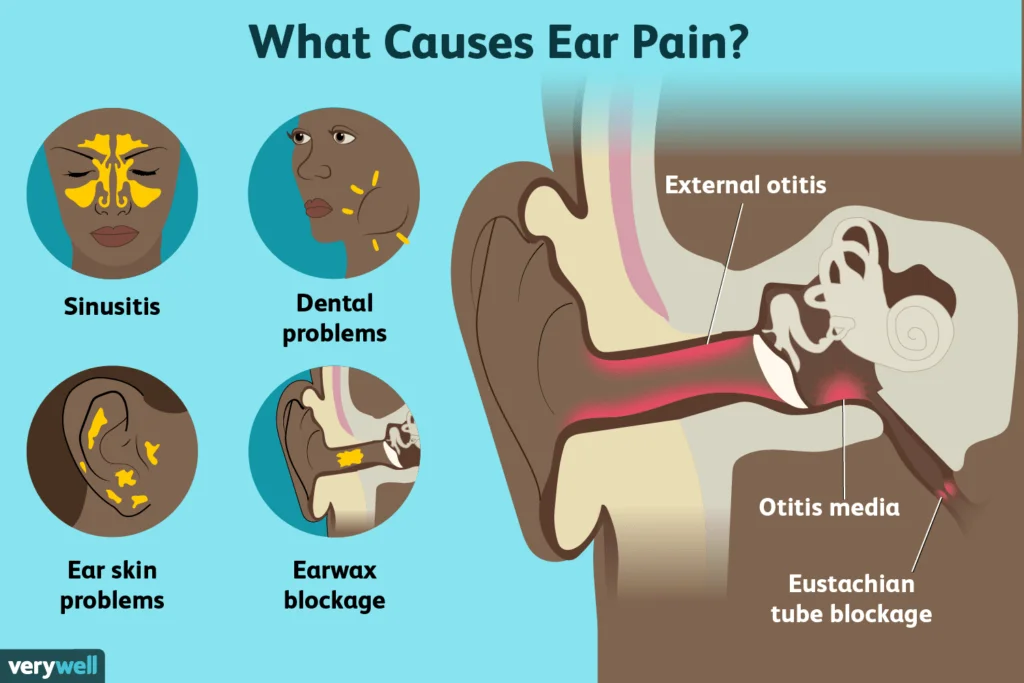
Fluid drainage from the ear can occur when an ear infection leads to fluid buildup behind the eardrum. This fluid can sometimes leak out of the ear, particularly if the eardrum becomes perforated.
In most cases, the fluid drainage is a clear or slightly yellowish discharge, but it can also be thicker and darker in color, depending on the type of infection. If you notice fluid draining from your ear, it’s important to seek medical attention right away, as this could be a sign of a more serious infection, such as a ruptured eardrum.
While fluid drainage may provide some temporary relief by reducing the pressure in the ear, it should never be ignored, as untreated ear infections can lead to further complications, including persistent ear infections and damage to the ear structures.
6. Fever or General Malaise
In some cases, ear infections can be accompanied by fever, especially if the infection is caused by bacteria. A fever can signal that your body is fighting the infection and working to get rid of the harmful bacteria or virus.
Along with fever, you may also experience a general feeling of being unwell (malaise), fatigue, or irritability. While these symptoms are more common in children, adults can also experience them during an ear infection.
If you develop a fever or feel generally unwell along with other symptoms like ear pain or drainage, it’s important to consult your doctor. A fever can sometimes be a sign that the infection is more severe or spreading, requiring medical attention and possibly prescription medication.
Preventing Ear Infections
While ear infections may not always be avoidable, there are several preventive measures you can take to reduce your risk. Here are some tips to help protect your ears and maintain good ear health:
- Keep Your Ears Dry: Excess moisture in the ears can create an environment where bacteria and fungi can thrive. After swimming or showering, gently dry your ears with a towel or use earplugs if you’re prone to swimmer’s ear.
- Avoid Inserting Objects Into Your Ears: Never insert cotton swabs or other objects into your ear canal. This can irritate the skin, push wax deeper into the ear, and increase the risk of infection.
- Manage Allergies: Allergies can increase your risk of ear infections by causing fluid buildup and inflammation in the sinuses and ears. If you suffer from allergies, work with your doctor to manage your symptoms effectively.
- Treat Respiratory Infections Early: If you catch a cold, flu, or sinus infection, try to manage it early with rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medications. Preventing these infections from worsening can help prevent them from spreading to the ears.
- Use Ear Protection in Noisy Environments: Loud noises can damage the delicate structures inside your ears. If you work in a noisy environment or are attending a concert, wear ear protection to prevent hearing loss.
- Boost Your Immune System: A strong immune system can help prevent infections, including those in the ear. Eat a balanced diet, exercise regularly, and get plenty of sleep to support your immune health.
When to See a Doctor
If you notice any of the symptoms mentioned above, it’s important to see a doctor, especially if the symptoms persist for more than 48 hours. Early detection and treatment can help prevent complications and ensure the infection is properly managed.
If you experience severe pain, fever, fluid drainage, or any hearing loss, don’t hesitate to seek medical attention. Ear infections may be treated with antibiotics if bacterial, or with over-the-counter medications to manage symptoms. In some cases, more severe infections may require a visit to an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist.
Conclusion
Ear infections are common but treatable. By being aware of the signs—such as itchiness, redness, pain, hearing loss, fluid drainage, and fever—you can take the necessary steps to seek prompt treatment. Preventive measures, such as keeping ears dry and managing allergies, can also help protect your hearing and reduce the risk of future infections.
If you experience any symptoms of an ear infection, don’t delay seeking medical care. By addressing the issue early, you can prevent complications and keep your ears in good health for years to come. Stay vigilant, and protect your hearing!






